-
What is contraception?
Contraception is the voluntary limiting of producing offspring by artificial methods. It is done to restrict the number of children and to increase the spacing between them.
-
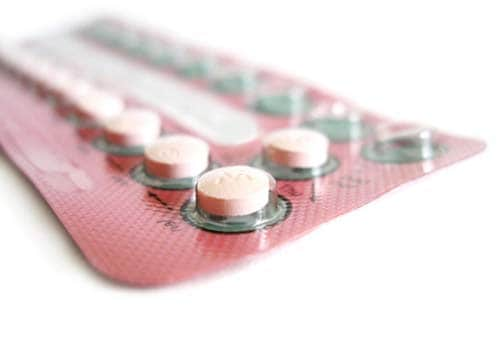
What are the various methods of birth control?
Methods of birth control may be temporary or reversible, or they may be permanent. Some of the reversible methods of contraception are:
Natural family planning methods
• Abstinence
• Withdrawal
• Rhythm method
Barrier method
• Condoms
• Diaphragms or cervical caps
• Intra-uterine devices
• Hormonal treatment
Oral Contraceptives
• Combined hormonal contraceptions
• progesterone only
• non-steroidal contraceptives
• postcoital or emergency contraception
Permanent birth control may be achieved by the process of sterilisation where the reproductive tubes of the man or the woman are blocked by surgery.- Abstinence – refraining from sex is the best way of contraception and is the only method that is 100 percent foolproof. The couple should not have vaginal sex during the period of abstinence, but other sexual forms of display of love like foreplay, may be continued. For obvious reasons this is not a long term solution.
- Withdrawal method – the withdrawal method, medically called coitus interruptus, is another temporary method of birth control. In this method, the man withdraws his penis from the woman’s vagina before ejaculating. However, this method has a high rate of failure for two reasons. Firstly, it does not provide satisfaction to the couple and secondly, a small amount of sperm may be ejaculated in the vagina before the penis is removed resulting in pregnancy.
- Rhythm method – in this method, the couple abstain from sex during the fertile period of the woman’s menstrual cycle. In women who have a menstrual cycle of 28 days, the 14th-16th days of the cycle are the most fertile as it is during this time that ovulation (release of eggs from the ovaries), takes place. The unsafe period extends from the 11th –18th days of the cycle keeping in view the lifespan of the sperms and the ovum. The days just after a period finishes are considered the safest. This method is not very reliable since most women do not have regular, predictable cycles.
- Condoms – condoms generally refer to synthetic rubber sheaths that cover the penis. Female condoms are also available that cover the external genitals and walls of the vagina. Condoms prevent the semen from being deposited in the vagina and thus prevent the contact of the sperm with the egg. Condoms are worn over the erect penis just before penetration. After sexual intercourse, the shaft has to be removed when it is still erect so that the condom comes out with it. The semen collects in the tip of the condom and should be carefully removed. Female condoms are to be inserted into the vagina before sex. The sheath that covers the external organs has rings on either side. One ring is inserted into the vagina while the other is left hanging outside to facilitate its removal. Condoms provide considerable safety if used properly. A condom should never be re-used.
- Diaphragms or cervical caps – a diaphragm is a dome shaped rubber barrier that can be inserted into the vagina and it fits snugly onto the cervix. A cervical cap also serves the same purpose. They have to be used with a spermicidal cream or jelly, which performs the dual function of killing any sperm and providing lubrication. However, these should always be used after consultation with the doctor since their use can be harmful in certain conditions like urinary tract infections.
- Intra-uterine devices – IUD’s are small devices that are inserted and left inside the uterus as a measure against conception. An IUD is most commonly a T-shaped device made of plastic with copper wires around all its arms (Copper T). It can be placed inside the uterus only by a trained professional and can remain active over a period of ten years.
- Hormonal treatment – hormonal treatment is given in the form of hormone injections. These shots are given every 3 months. This is a progestin injection which is given in the arm or the buttocks.
- Oral contraception – or birth control pills, are the most common form of contraception. These pills are taken everyday for a specified period of time to prevent pregnancy. Oral contraceptives work by preventing the ovaries from releasing the eggs. The pills use a combination of the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which are taken for 21 to 25 days in a month. If a woman on pills wishes to conceive, she must discontinue the pills and use another method of contraception for at least 4-6 weeks before conceiving.
Permanent method of birth control:
- Sterilisation – it is a surgical method of birth control for both men and women. The most common procedure is the tying up of the tubes i.e., the Fallopian tubes in women (tubectomy) and the vas deferens (vasectomy) in men. Surgical sterilisation may be performed by removing the ovaries, all or part of the fallopian tubes or the uterus itself (hysterectomy). After a vasectomy, for the first two weeks it is recommended that another method of contraception like condom can be used.
- Abstinence – refraining from sex is the best way of contraception and is the only method that is 100 percent foolproof. The couple should not have vaginal sex during the period of abstinence, but other sexual forms of display of love like foreplay, may be continued. For obvious reasons this is not a long term solution.
-

What are the advantages of birth control?
Birth control is a way by which couples can regulate the size of their families. Apart from social advantages, family planning helps to preserve the health of women. Advantages of the various methods of birth control have to be listed according to the method of contraception.
- Oral contraception:
- Prevents pregnancy
- Regulates the menstrual cycle
- Decreases premenstrual symptoms
- Helps in certain skin conditions like acne.
- Condoms:
- Help prevent pregnancy and STDs
- Are inexpensive and easy to acquire
- Do not require a prescription
- Are not dependent on any physical condition.
- Diaphragms and cervical caps:
- Do not interrupt the sex act if inserted well in time
- Are usually not felt by either partner during sexual intercourse.
- Do not interrupt the sex act if inserted well in time
- IUDs:
- Are effective and long term methods of birth control
- Do not usually cause complications since they are inserted by a medical health professional
- Do not interrupt regular sexual relations in any way.
- Are effective and long term methods of birth control
-

What are the side effects/disadvantages?
- Oral contraception:
- Headaches
- Breast tenderness and discharge
- Weight increase
- Fatigue and mood swings
- Condoms:
- Some people feel that the sensation dulls with the use of a condom
- The sexual excitement phase has to be given a break to wear the condom on the erect penis
- Some men are self-conscious about using condoms.
- Diaphragms and cervical caps:
- There may be difficulty in insertion of the diaphragm
- In some positions, the diaphragm may get dislodged
- It may cause irritation.
-

What are the factors to be considered while choosing a contraceptive?
- Availability – the contraceptive should be easily available in the locality.
- Cost effectiveness – the contraceptive must be cost effective, in that it should provide maximum service at the lowest cost.
- Health risk – the methods of birth control must not be harmful for the user.
- Effectiveness – the contraceptive must protect against what it is proposed to protect. It must also be chosen according to the urgency with which the results are sought. In case an unwanted pregnancy has potentially devastating results, a more robust method must be chosen.
- Partner involvement – both the partners must be willing to embrace the method of birth control chosen.
- Availability – the contraceptive should be easily available in the locality.

















