Though it is quite rare, moles can turn into melanoma, which is known to be a serious kind of skin cancer.
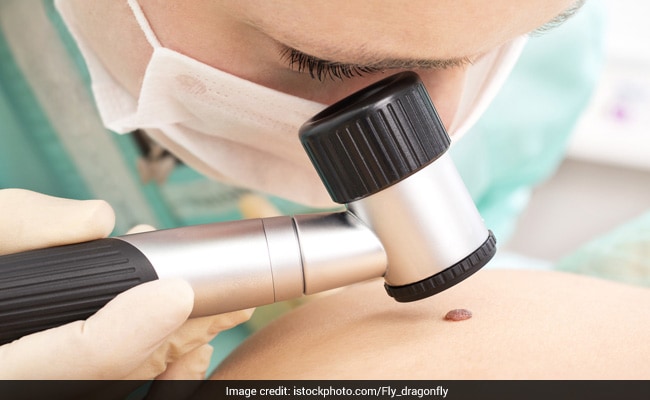
It is quite rare that moles become cancerous
HIGHLIGHTS
- It is said that people continue to develop moles up until the age of 40
- It is quite rare that moles become cancerous
- Excess exposure to sun's rays can increase risks of melanoma
Moles are growth on the skin which develops when pigment cells grow in clusters. Moles usually grow in areas above the waist which are exposed to the sun. Breast, scalp and buttocks are areas where moles rarely develop. Some moles are on the body since birth, but others appear later in life. It is said that people continue to develop moles up until the age of 40. Moles are also known as nevus or nevi (plural). While some of these moles fade away with age, there are others which stay on the body forever.

Excessive exposure to sun's rays can make moles cancerous
Photo Credit: iStock
A common mole is going to be around 5 mm wide, which is about 1/4th the size of an inch. It is as small as a pencil eraser.
Can a mole become cancerous?
Though it is quite rare, moles can turn into melanoma, which is known to be a serious kind of skin cancer. While common mole is not cancerous, people with more than 50 common moles are more prone to risks of melanoma. There are a few symptoms which tell if your mole is becoming cancerous or not. These symptoms include colour changes in the mole, mole getting unevenly smaller or bigger, mole changing shape, texture or height, skin of the surface of the mole becoming dry or scaly, mole becomes hard or lumpy, if it starts to itch or if it bleeds or oozes are all sign of cancerous mole.
Also read: 7 Reasons For White Spots On Your Skin
Dysplastic nevus
A dysplastic nevus is a kind of mole which may be bigger than a common mole and have a different colour, surface and border. This kind of mole is usually smooth and slightly scaly. It has a pebbly surface and an irregular edge which fades in the surrounding skin.
This kind of mole can occur anywhere in the body, but usually happen in areas exposed to the sun. But it can also appear in areas which are not exposed to the sun, such as scalp, breasts and areas below waist.
Most dysplastic nevus do not turn cancerous. They remain stable over time. However, research says that people with more than 5 dysplastic nevi are at high risks of developing melanoma.
People with dysplastic nevus should avoid getting suntan or sunburn. Dermatologists recommend that people with dysplastic nevi should get their skin checked regularly. Symptoms of a dysplastic nevi turning cancerous are same as a common mole turning cancerous.
People usually do not get their moles because they don't turn cancerous. Another reason for not removing common moles or dysplastic nevi is that their removal does not prevent melanoma development.
Also read: These Mistakes Are Making Your Skin Age Faster
What is Melanoma
Melanoma is a dangerous skin cancer because it can spread to other parts of the body such as liver, lungs, bones and brains. Like most cancers, it is considered beneficial if the melanoma is detected and removed timely. Melanoma can develop from a common mole or dysplastic nevus. It can even develop on normal skin, the cancer can also develop in the digestive tract, eyes and various other parts of the body.
In men, melanoma develops on neck, head and back, while in women, it develops on the back or lower legs. People with light skin are more likely to develop melanoma as compared to people with dark skin.
Also read: 6 Foods To Eat For Glowing Skin
Factors that increase chances of melanoma
People with dysplastic nevus or people with more than 50 common moles are at high risks of developing melanoma.
1. Sunlight
Ultraviolet rays of the sun can be harmful for the skin. They can cause melanoma and various other kinds of skin cancer. People who have severe blistering or sunburns are at higher risk of developing cancerous moles. People who get tanned without sunburn are at higher risk of developing melanoma.

UV rays of the sun can increase risks of melanoma
Photo Credit: iStock
2. Skin that burns easily
People who have skin that burns quite easily are more prone to risks of melanoma as compared to others. This includes people who have a pale skin who have many freckles, have red or blonde hair and blue or grey eyes.
3. Some medicines
Some antibiotics, anti-depressants and hormones can make your skin more sensitive and increase chances of you developing melanoma. These medicines make the skin more sensitive to the sun and suppress the body's immune system.
Some medicines can increase risk of melanoma
Photo Credit: iStock
4. Family history
People who have melanoma in family history are more prone to risks of melanoma. If you have 2 or more family members with melanoma, you are at higher risk of developing it.
Disclaimer: This content including advice provides generic information only. It is in no way a substitute for qualified medical opinion. Always consult a specialist or your own doctor for more information. NDTV does not claim responsibility for this information.
DoctorNDTV is the one stop site for all your health needs providing the most credible health information, health news and tips with expert advice on healthy living, diet plans, informative videos etc. You can get the most relevant and accurate info you need about health problems like diabetes, cancer, pregnancy, HIV and AIDS, weight loss and many other lifestyle diseases. We have a panel of over 350 experts who help us develop content by giving their valuable inputs and bringing to us the latest in the world of healthcare.














