Health Photos
-
STIs are infections that one gets by having sexual intercourse (vaginal, oral or anal) with someone who already has an STI. There are more than 30 different sexually transmissible bacteria, viruses and parasites. Several, in particular HIV and syphilis, can also be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy and childbirth, and through blood products and tissue transfer.
-
Bacteria and viruses cause STIs. Those caused by bacteria include chlamydia, gonorrhoea, trichomoniasis and syphilis. These can be treated and cured with antibiotics. STIs caused by viruses include HIV/AIDS, genital herpes, genital warts and cytomegalovirus. These STIs can be controlled but not cured.
-
Stay loyal to your partner as multiple sex partners increase your vulnerability of getting infected with sexually transmitted infections and diseases.
-
Most sexually transmitted diseases can be avoided to a large extent by practicing safe sex. Using condom is the best way of avoiding both STIs and unwanted pregnancy.
-
AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) is a disease that weakens the body's ability to protect itself from getting sick. The virus that causes it is HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), which is found mainly in blood but occurs in other body fluids such as semen, vaginal secretions and breast milk.
-
Gonorrhoea is an infection easily transmitted by sexual contact. The causative organism can infect the throat, producing severe soreness; the urethra, causing burning, painful urination and it may also infect the anus and the rectum. Untreated gonorrhoea may lead to urinary tract infections and ultimately kidney failure. The most common initial symptom is a thick discharge from the urethra, which may be white or yellow. There may be painful urination.
-
Syphilis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, which penetrates broken skin or mucous membranes. It can also be transmitted to the foetus via the placenta. It infects the genital area, lips, mouth, or anus of both men and women. One gets syphilis from sexual contact with someone who has it. It can also pass from mother to baby during pregnancy.
-
It is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. The majority of genital chlamydia infections are without symptoms until complications appear. Infection with chlamydia leads to pelvic inflammatory disease, which can cause scarring of the fallopian tubes and sterility. The symptoms include burning with urination, discharge from the end of the penis, tenderness or pain in the testicles, fever and chills.
-
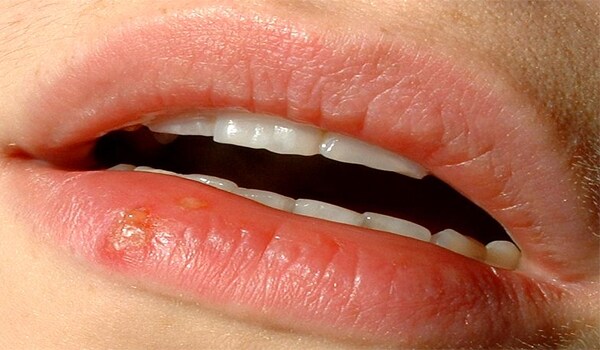
This is an infection caused by the Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-l) which is associated with infections of the lips, mouth and face. HSV-2 is associated with genital lesions and is transmitted by sexual contact. HSV-2 can be transmitted to a newborn during vaginal delivery if the mother is actively infected. Infection occurs after exposure to the virus through a break in the skin, or through mucous membranes. The virus spreads to nerve cells within the body and then to other skin surfaces. The symptoms include genital lesions, fever, vaginal discharge, sore throat and in some cases memory loss.
-
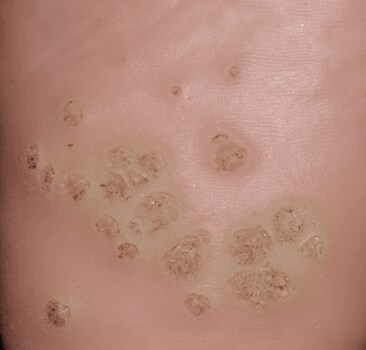
Genital warts are caused by the Human papilloma virus (HPV) which causes small growths on the skin and mucous membranes. They grow best in moist genital areas and are flesh-coloured tumours appearing singly or in clusters. In women, HPV can invade the vagina and cervix and may lead to cancerous changes in the cervix.
-
Trichomoniasis is caused by a parasite. It affects both women and men, but symptoms are more common in women. Symptoms include a green or yellow discharge from the vagina, itching in or near the vagina and discomfort with urination. Most men with trichomoniasis don't have any symptoms, but it can cause irritation inside the penis.
-
- Having a mutually monogamous sexual relationship with an uninfected partner.
- Correctly and consistently using a condom greatly reduces the chance of acquiring an STI.
- Using clean needles if injecting intravenous drugs.
- Having regular check ups for STIs even in the absence of symptoms.
-
Anyone diagnosed as having an STI should:
- Be treated to reduce the risk of transmitting an STI, especially a pregnant woman to an infant.
- Follow the full course of medicine.
- Avoid sexual activity while being treated for an STI.
- Ensure that the partner is also diagnosed and treated.