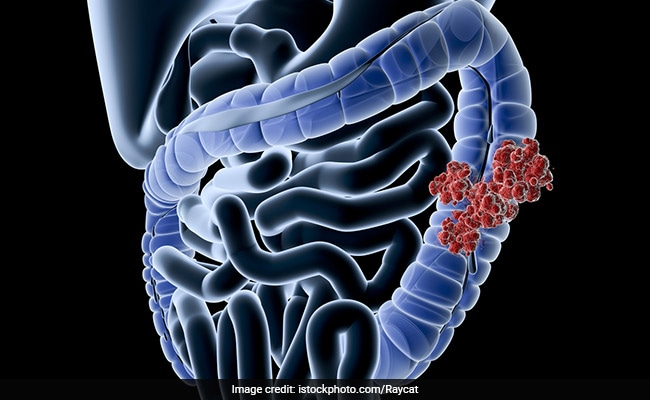
World Cancer Day 2023: Most colorectal cancers begin as a growth on the lining of the colon or rectum. The rectum is the lower part of our digestive tract which is responsible for the absorption of salt and water from remaining food that has passed through the small intestine.
World Cancer Day is observed on February 4 very year
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common cancer all over the world. It is the third most common cancer in men and the second most common cancer in women, with more than 1.4 million new cancer cases diagnosed each year. Most colorectal cancers begin as a growth on the lining of the colon or rectum. The rectum is the lower part of our digestive tract which is responsible for the absorption of salt and water from remaining food that has passed through the small intestine. This remaining food is stored in the rectum and is passed out as stools from the body.
The growth of cancer cells in the colon or rectum is known as polyps. Some polyps can develop into cancer over time (usually many years), but not all polyps are like that. The likelihood of a polyp developing into cancer is determined by the type of polyp.
If cancer develops in a polyp, it can spread to the colon or rectum wall over time. The colon and rectum walls are made up of many layers. It can begin in the innermost layer (the mucosa) and can spread to any or all the other layers such as they can develop/ spread to blood vessels, lymph vessels and other distant parts of the body. A colorectal cancer's stage (the extent to which it has spread) is determined by how deeply it has grown into the wall and whether it has spread outside the colon or rectum.
Risk factors
The modifiable risk factors include- being obese, lack of physical inactivity, people having rick of red, and processed meats, smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
The non-modifiable risk factors include old age, personal history of adenomatous polyps, family history of colorectal cancer, inherited syndromes and ethnicity.
Prevalence in India
Colorectal cancer has a low age standardized rate (ASR) in India, at 7.2 per 100,000 population in men and 5.1 per 100,000 population in women. Colorectal cancer affects approximately 4 people per 100,000 people.
Early symptoms of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer may not cause obvious symptoms right away, but if it does, it may cause one or more of the following:
- A change in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, or stool narrowing that lasts more than a few days
- A need for a bowel movement that isn't relieved by having one
- Rectal bleeding with bright red blood
- Blood in the stool, which may cause the stool to appear dark brown or black
- Cramping or abdominal (belly) pain
- Weakness and fatigue
- Unwanted weight loss
In some cases, colorectal cancers may often lead to bleeding in the digestive tract. Sometimes the blood can be seen in the stool or make it look darker. However, over time, the blood loss can build up and can lead to low red blood cells in the body.
Steps for prevention
Colorectal cancer screening- Screening is the process of detecting cancer or pre-cancer in people who do not have symptoms of the disease. One of the most effective tools for preventing colorectal cancer is regular colorectal cancer screening.
Avoiding modifiable risk factors by living a healthy lifestyle and avoiding unhealthy practices
Genetic testing is also recommended if you have a known family history of colorectal cancer.
Treatment options
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, different types of treatment may be combined at the same time or used after one another. The treatment includes-
Colonoscopy (polypectomy) - If a cancer is small, localized, completely contained within a polyp and in a very early stage, a doctor may be able to remove it completely with the help of a colonoscopy
Endoscopic mucosal resection - This is used for removing larger polyps with the help of performing colonoscopy which uses special tools to remove the polyp and a small amount of the inner lining of the colon. This process is called an endoscopic mucosal resection
Minimally invasive surgery (laparoscopic surgery) - This is used for removing the polyps that can't be removed during a colonoscopy. A surgeon performs the operation through several small incisions in the abdominal wall, inserting instruments with attached cameras that display the colon on a video monitor. The surgeon may also take samples from lymph nodes in the area where the cancer is located.
(Dr Deeksha Kapoor, Consultant, GI Surgery, GI Oncology and Bariatric Surgery , Institute of Digestive and Hepatobiliary Sciences, Medanta, Gurugram)
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed within this article are the personal opinions of the author. NDTV is not responsible for the accuracy, completeness, suitability, or validity of any information in this article. All information is provided on an as-is basis. The information, facts, or opinions appearing in the article do not reflect the views of NDTV and NDTV does not assume any responsibility or liability for the same.
DoctorNDTV is the one stop site for all your health needs providing the most credible health information, health news and tips with expert advice on healthy living, diet plans, informative videos etc. You can get the most relevant and accurate info you need about health problems like diabetes, cancer, pregnancy, HIV and AIDS, weight loss and many other lifestyle diseases. We have a panel of over 350 experts who help us develop content by giving their valuable inputs and bringing to us the latest in the world of healthcare.














