-
What are fungal infections of the skin?
Skin fungi live in the dead, top layer of skin cells in moist areas of the body, such as between the toes, groin, and under the breasts. These fungal infections cause only a slight irritation. Other types of fungal infections penetrate deeper and may cause itching, swelling, blistering, and scaling. In some cases, fungal infections can cause reactions elsewhere on the body. For example, a person may develop a rash on the finger or hand after touching an infected foot.
-
What are the various types of fungal skin infections?
There are many types of fungal skin infections. Listed below are some:
- Candidiasis (Yeast Infection)
- Tinea infections (Ringworm)
- Tinea versicolor
-
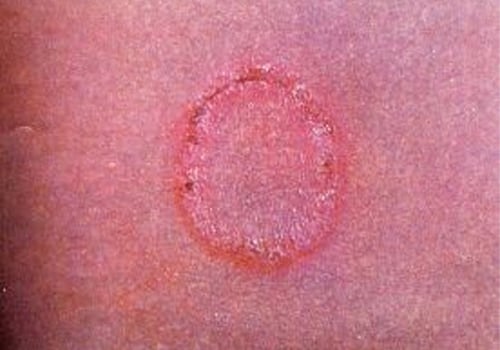
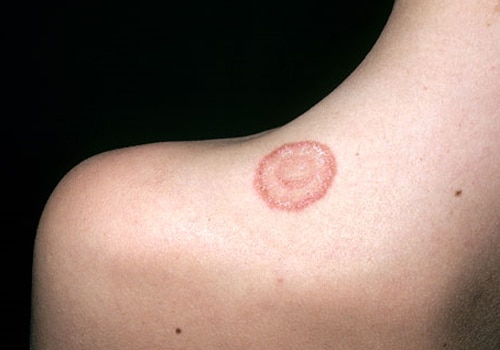
Tinea infections (Ringworm)
Different fungi, depending on their location on the body, cause ringworm. Ringworm is characterised by ring-shaped, red, scaly patches with clearing centers. There is an increased risk of contracting ringworm if a person:
- is malnourished
- has poor hygiene
- lives in a warm climate
- has contact with other persons or pets that have ringworm
- is immunocompromised by disease or medication
- Jock itch (tinea cruris or groin ringworm)- This condition is also more common in males and occurs more often during warm weather conditions. It is very rare in females. Symptoms of jock itch may include red, ring-like patches, pain and itching in the groin area. Treatment involves keeping the affected area clean and dry and applying topical antifungal medications. Jock itch usually responds to over-the-counter antifungal creams and sprays.
- Athlete's foot (tinea pedis or foot ringworm) - This common condition mostly affects teen and adult males. Contributing causes include sweating, not drying the feet well after swimming or bathing, wearing tight socks and shoes, and warm weather conditions. Symptoms of athlete's foot may include whitening of the skin between the toes, scaling of the feet, itchy rash and blisters on the feet. Athlete's foot is treated with topical antifungal medication in most cases. Severe cases may require oral medications. The feet must be kept clean and dry, as the fungus grows in moist environments.
- Scalp ringworm (tinea capitis) - Scalp ringworm is highly contagious, especially among children. It occurs mainly in children between the ages of 2 to 10 years. It rarely occurs in adults. Symptoms of scalp ringworm include red, scaly rash on the scalp along with itching and hair loss. Ringworm of the scalp can also develop into a kerion, a large, tender lesion over the area of the initial ringworm. This is caused by a hypersensitivity to the ringworm and may be associated with a rash elsewhere and tender lymph nodes in the neck.
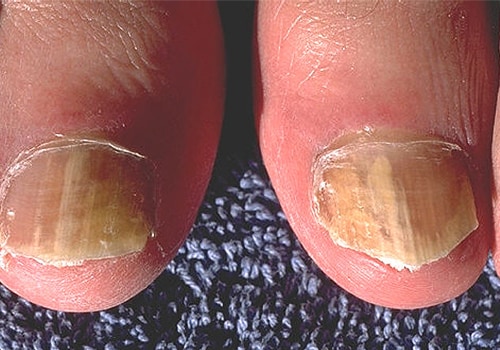
- Nail ringworm (tinea unguium) An infection of the finger or toe nail, characterised by a thickened, deformed nail. This condition more often affects the toenails than the fingernails. This occurs more often in adolescents and adults rather than young children. Symptoms of nail ringworm include thickening of the ends of the nails and a yellow colour to the nails.
- Body ringworm (tinea corporis) This skin infection is characterised by a ring-like rash anywhere on the body or the face. It occurs in all ages, but is seen more frequently in children. It is more common in warmer climates. The symptoms include red, circular lesion with raised edges. The middle of the lesion may become less red as the lesion grows and there is associated itching.
Treatment for scalp ringworm (tinea capitis) may include an oral anti-fungal medication that is usually prescribed for four to eight weeks. This also involves the use of a special shampoo, to help eliminate the fungus. If a kerion is present (a large, tender, swollen lesion), additional medications, such as steroids maye be given to help reduce the swelling. Treatment for ringworm of the body, groin, and foot is usually a topical anti-fungal agent or an oral antifungal medication. The length of the treatment depends on the location of the ringworm. Because the fungi can live indefinitely on the skin, recurrences of ringworm are likely. Treatment may need to be repeated.
-
Tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor is a common fungal skin infection characterised by lighter or darker patches on the skin. Patches are most often found on the chest or back and prevent the skin from tanning evenly. It occurs mostly in adolescence and early adulthood, but it can occur at any time. Usually, the only symptom of tinea versicolor is the white or light brown patches. Patches may scale slightly, but rarely itch or hurt. Other common characteristics of the rash include:
- white, pink, or brown patches
- infection only on the top layers of the skin
- the rash usually occurs on the trunk and not the face
- patches worsen in the heat, humidity, or if you are on steroid therapy or has a weakened immune system
- patches are most noticeable in the summer
Treatment usually includes the use of dandruff shampoo on the skin. The shampoo is left on the skin overnight and washed off in the morning. To be effective, the shampoo treatment may be required for several nights. Tinea versicolor usually recurs, requiring additional treatments. Topical creams or oral antifungal medications may also be needed. It is also important to know that improvement in the skin may only be temporary, and a recurrence of the condition is possible. The treatment will not bring the normal color back to the skin immediately. This will occur naturally and may take several months. -
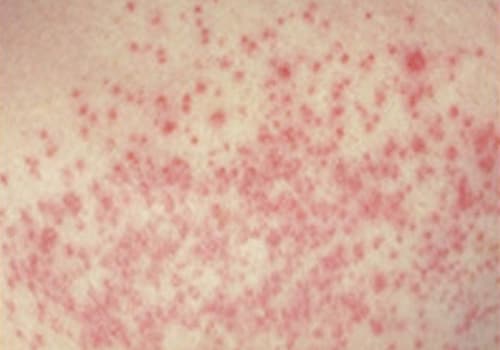
Candidiasis (Yeast Infection)
Candidiasis, sometimes called moniliasis or yeast infection, is an infection caused by yeast on the skin and/or mucous membranes. Although yeast is normally a harmless inhabitant of the digestive system and vaginal area, it may cause an infection when the skin is damaged, when conditions are warm and humid, and/or when a person has a depressed immune system. The symptoms of candidiasis vary depending on the location of the infection. The most common symptoms of a yeast infection are:
- skin folds or navel: rash, patches that ooze clear fluid, pimples, itching or burning
- vagina: white or yellow discharge, itching, redness in the external area, burning
- penis: redness, scaling and painful rash on the underside of the penis
- mouth (thrush): white patches on tongue and inside of the cheeks, pain
- corners of the mouth (perlèche): cracks and/or tiny cuts at the corner of the mouth
- nail beds: swelling, pain and pus, white or yellow nail that separates from the nail bed
Candidiasis is highly treatable with medicated ointments. Yeast infections in the vagina or anus can be treated with medicated suppositories. Thrush may be treated with a medicated mouthwash or lozenges that dissolve in the mouth. Severe infection or infections in an immunocompromised person may be treated with oral anti-yeast medications.

















