-

What is urine albumin?
Albumin is a protein present in the blood. Proteins are normally absent in urine because the kidney cells generally prevent large molecules including proteins, from being excreted. Some proteins may appear in the urine in normal individuals also if blood levels are very high. In kidney diseases, albumin will appear in the urine even with normal blood levels. The test for urinary albumin measures the amount of protein in urine.
-
How is it tested?
Urinary protein (albumin) can be tested in a random sample of urine collected in clean, dry container or quantitatively in a 24-hour sample. For collecting a 24 hour sample, urine collection is started, in a large clean container e.g. a jerry can, after the morning urination. All subsequent urine is collected for the next 24 hours, including the morning sample on the second day. The container should be kept capped in the refrigerator or a cool place during the collection period and labelled with the patient’s name, date, time of completion, and handed over to the laboratory for testing.
Urinary albumin is tested in the laboratory by a simple dipstick (qualitative method - a colour change signifying the presence of albumin) or a quantitative method. -
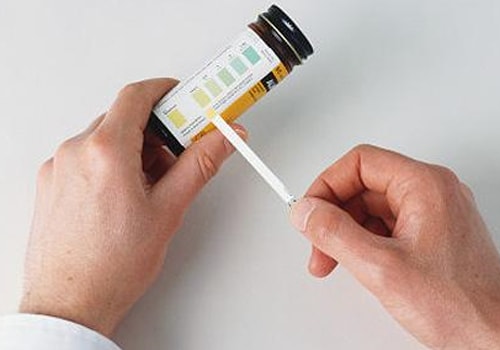
Why is it tested?
This test is usually done to check the functioning of the kidneys. It is also used as a basic screening test.
-
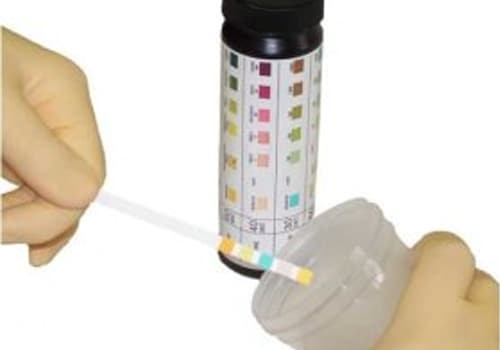
What are the normal values?
0 to 8 milligrams per decilitre (mg/dl).
OR
50-80 milligrams per 24-hours (mg/24-hrs), at rest
(>250 mg/24-hrs, after strenuous exercise) -

What are the abnormal values?
Increased urinary protein may be due to:
- Kidney diseases like glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, nephritic syndrome, diabetic nephropathy
- Blood pressure, Preeclampsia and Eclampsia
- Congestive heart failure
- Heavy metal poisoning
- Multiple myeloma
- Treatment with drugs causing injury to the kidneys like aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, polymyxin B, colistin, griseofulvin, lithium, penicillamine, aspirin, sulfonamides, etc
- Emotional stress, strenuous exercise or improper collection (contamination of urine with vaginal secretions)
- Radiopaque contrast media (used for special X-rays or CT scans) in the previous 3 days
- Kidney diseases like glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, nephritic syndrome, diabetic nephropathy

















