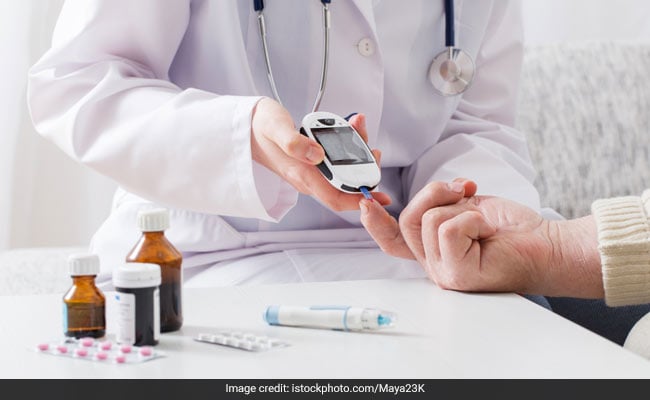
Type 2 Diabetes dis
Type 2 Diabetes
What is it?
 Type 2 diabetes: Insulin resistance is the main reason responsible
Type 2 diabetes: Insulin resistance is the main reason responsible
Type 2 (DM2), earlier known as non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or adult-onset diabetes. This is the most common form of diabetes, and is strongly associated with genetic tendency and obesity. The body produces normal or even high levels of insulin, but certain factors make its utilization ineffective ("insulin resistance"). Sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy dietary patterns, and the consequent obesity are common causes. It usually starts in adulthood, but is beginning to be seen in obese adolescents also.
What are the causes?
 Type 2 diabetes: Increase in blood sugar levels can result in this condition
Type 2 diabetes: Increase in blood sugar levels can result in this condition
Type 2 diabetes is a long term condition so identifying the exact cause responsible for this condition cannot be quoted. Insulin resistance is the main cause responsible for type 2 diabetes. When a person's body stops responding to insulin the way it should, the blood sugar levels increase and that develops into type 2 diabetes over a period of time.
What are the symptoms?
 Type 2 diabetes: Symptoms include frequent thirst
Type 2 diabetes: Symptoms include frequent thirst
- Increased thirst
- Frequency of Urine
- Extreme tiredness
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Genital itching or regular episodes UTI
- Slow healing of wounds
- Excessive hunger
What are the risk factors?
A risk factor refers to anything which can make a person more prone to a particular condition. For type 2 diabetes, a number of factors can increase your risk of developing this condition. The most important risk factors of type 2 diabetes are as follows:
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Cholesterol
- Family history
- History of gestational diabetes
What is the treatment?
Type 2 is initially treated with weight reduction, diet control and regular exercises. When these measures fail to control the blood sugar levels, oral medicines are used. Sulphonylureas are a group of drugs that stimulate the release of insulin from the pancreas. Metformin reduces insulin resistance, and the production of glucose by the liver. Thiazolidenediones also increase insulin efficiency and sensitivity. Acarbose delays the absorption of glucose by the intestines. When the action of oral drugs is insufficient, insulin injections are added.
What are the prevention?
Type 2 diabetes is quite preventable if you follow a healthy lifestyle. A balanced diet and a good workout routine can significantly reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Some more tips to prevent type 2 diabetes are:
- Manage weight
- Check blood sugar levels regularly
- Stick to a balanced diet
- Quit smoking
- Limit alcohol intake
- Limit the consumption of processed foods
What are the complications?
A person dealing with type 2 diabetes needs to take important steps to keep blood sugar levels under control. Failure to control blood sugar can result in serious health complications in a person dealing with type 2 diabetes. These complications can be both short term and long term. Short term complications in type 2 diabetes include retinopathy, kidney problems, cataracts and damage to the nerves. Long term complications of type 2 diabetes include increased risk of strokes, heart attacks and peripheral vascular disease.
What is the homecare treatment?
Type II diabetes can be treated with diet and exercise alone, or these with medicines (oral hypoglycaemic agents) and/or insulin. People with type II diabetes may also be overweight. Weight loss and regular exercise may reduce the blood sugar, need for medication and enable your body to use insulin better.
For type II clients with high morning blood sugars, exercising in the evening (after four p.m.) may help; it is thought that the evening activity may stop your liver from producing excess sugar during the night.
Type 2 Diabetes News More News
- Once-A-Week Insulin Treatment Could Be Highly Beneficial For Diabetes Patients: Study
- Heart Patients Three Times More Likely To Have Diabetes: Study
- Cholesterol Might Hold Key To New Therapies For Diabetes, Alzheimer's Disease
- Weekly Insulin Helps Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Achieve Similar Results To Daily Insulin
- Obesity Raises Type 2 Diabetes Risk In Women With PCOS, Says Study
- Type 2 Diabetes: Regular Exercise Can Be Effective For Prevention
- Overweight, Diabetic People At Risk Of Developing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- More Than Half Of People In Their Twenties In Urban India Likely To Develop Diabetes In Lifetime: Study
- Diabetic Eye Disease Associated With High Risk Of Severe COVID-19, Finds Study
Type 2 Diabetes Health Photos More Photos
Type 2 Diabetes Videos More Videos
FAQ Related to Type 2 Diabetes
- I am diabetic; can I take jaggery?
- What is the cause for high ESR?
- Is my diabetes due to insulin deficiency or insulin resistance?
- Why does my brother have low platelet count?
- Am I taking correct treatment for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)?
- What care should be taken by a pre-diabetic while planning a baby?
................... Advertisement ...................
................... Advertisement ...................
................... Advertisement ...................
................... Advertisement ...................