Hepatitis
What is it?
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver cells due to a viral infection of the liver or injury caused by a chemical toxin.
What are the causes?
Hepatitis is caused by many viruses. The most common being: Hepatitis A virus- this is most common in children and is present in the stools of infected individuals. When someone eats food that is contaminated with HAV-infected stool, the virus passes into the body. Hepatitis spreads easily in unsanitary living conditions and contaminated water, milks and foods. Hepatitis B virus- is also called “serum hepatitis”. HBV spreads through infected body fluids such as blood, saliva and breast milk. Infection occurs through contaminated blood transfusion, shared contaminated needles or syringes. Hepatitis C virus usually develops after a contaminated blood transfusion but may also spread through sexual contact.
What are the symptoms?
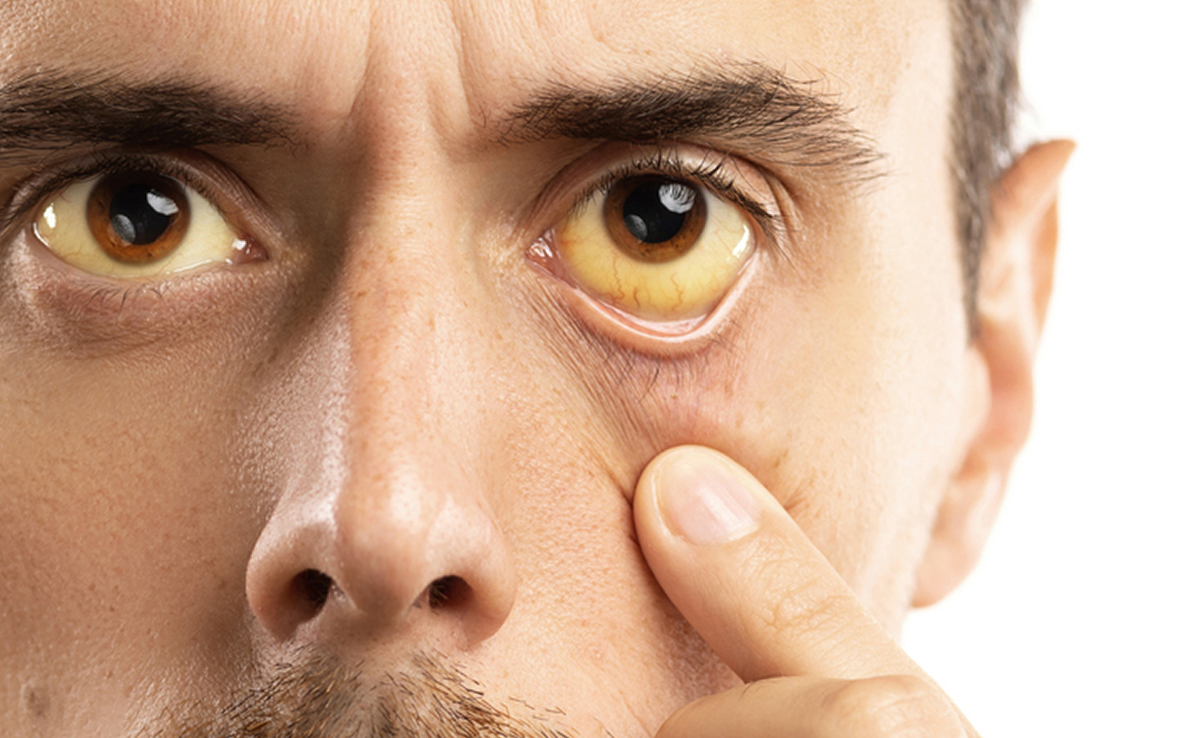
In the early stages it may cause flu-like symptoms such as general weakness, loss of appetite, diarrhoea and muscle aches. If it progresses the chemicals normally secreted by the liver build up in the blood causing jaundice (a yellowing of the skin and eyes), foul breath and a bitter taste. The urine turns dark and stools become clay coloured. There can be abdominal pain. Although many cases of hepatitis resolve with treatment, the disease can sometimes lead to death.
How is the diagnosis made?
The symptoms usually develop over a period of several days. Children who are infected often have no symptoms. The symptoms may be: Yellowing of the eyes and dark urine. General tiredness and poor appetite. Nausea, vomiting, fever and stomach ache.A person may spread HAV from about one week before symptoms appear and during the first week of symptoms. Persons with no symptoms can also spread the virus. Unlike Hepatitis B and C, Hepatitis A causes no long term liver damage. Having had the disease produces lifelong immunity from future HAV infection.
What is the treatment?
There are no specific treatments for the acute symptoms of viral hepatitis. Doctors recommend bed rests, a healthy diet, avoidance of alcoholic beverages and fatty foods. Medications may include vitamins and pills to reduce nausea and vomiting. Care must be taken to avoid any drug like contraceptive pills that may further cause injury to the liver cells.
What are the prevention?
Good personal hygiene and proper sanitation can help prevent the infection. Toilets and sinks need to be cleaned with antiseptic solutions. Hepatitis B is contagious and its main routes of infection are contaminated blood transfusions, shared needles for drug injections and sexual contacts. Use of vaccines greatly decreases the incidence of this infection.Hepatitis C infection may pass from mother to foetus during pregnancy. A great deal of awareness and caution along with the doctor’s advice is required to prevent this infection.
Hepatitis News More News
- Hepatitis Infections Lead To Chronic Liver Diseases; Follow These Preventive Tips
- World Hepatitis day: Hepatitis Action Plan To Be Rolled Out By October: Central Health Ministry
- World Hepatitis day: Hepatitis Still Prevalent Despite Vaccination
- Tattooing raises hepatitis C risk
- Coffee may slow liver damage from hepatitis
- Gujarat in the grip of Hepatitis B, 19 killed
- Glucose abnormalities in Hepatitis patients
- Hepatitis B linked to bile duct cancer
- Cannabis use worsens hepatitis C
FAQ Related to Hepatitis
................... Advertisement ...................
................... Advertisement ...................
................... Advertisement ...................
................... Advertisement ...................