-
What is bleeding?
Bleeding is the rupture of blood vessels due to any injury or cut. Bleeding may be external when it is from the surface of the body or internal when it is within the body cavity like bleeding within the chest, skull or abdomen. Bleeding may occur from arteries, veins, or capillaries or from a combination of these.
-

What are the causes of bleeding?
Bleeding may occur due to a cut by a sharp edge, wound caused by falling, or injury due to an accident. Internal bleeding can be due to a sudden rise in blood pressure.
-

What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of bleeding include:
- Blood comes out from the wound or injured part
- The patient feels faint and may collapse
- The skin becomes pale and cold
- The pulse gets rapid and weak
- The breath becomes shorter
- There may be profuse sweating
- The patient feels thirsty.
- Blood comes out from the wound or injured part
-
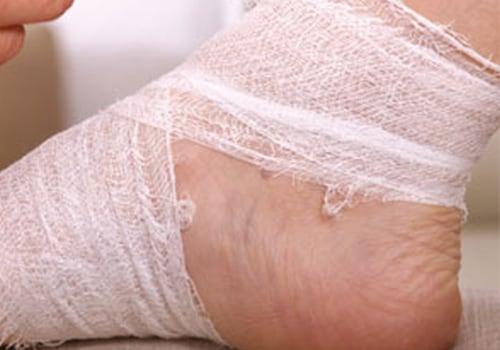
What first aid can be provided?
The aims of first aid are to stop the bleeding quickly and to get medical help immediately. First aid differs in case of internal and external bleeding. In case of external bleeding, the following steps should be followed:
- Place the patient in a comfortable position.
- Apply a clean pad of cotton larger than the size of the wound and press firmly with the palm until the bleeding becomes less or stops.
- If bleeding continues, add more pads of cotton without removing the older ones.
- When bleeding stops, clean the area with an antiseptic.
- Bandage firmly but not too tightly.
- The patient should be made to lie down with head in the low position and legs raised by placing the pillow under them.
- The patient should be made to feel relaxed and should not be allowed to move.
- Nothing should be given to eat or drink.
- Hot water bottles or ice bags should not be placed to make the patient feel comfortable.
- Patient should be taken to the doctor as soon as possible.
- Place the patient in a comfortable position.

















