-

What is dengue fever?
Dengue fever is an acute infectious viral disease, caused by all four types of dengue virus 1, 2, 3 and 4. It is transmitted by the bite of mosquitoes, most commonly Aedes aegypti found in tropical and subtropical regions.
-
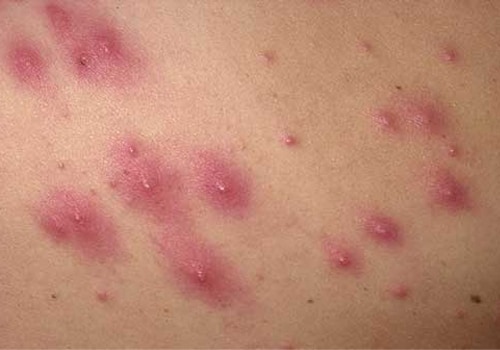
What are its symptoms?
- Fever, with a sudden onset, often rising to 40-40.5 degrees centigrade.
- Rash, which shows up 3-4 days after the start of the symptoms, starting from the trunk region and spreading to the face, arms and legs.
- Muscle aches (myalgia).
- Joint aches (arthralgia).
- Headache.
-

How is the condition diagnosed?
- Total white blood cells count: In case of dengue, this test will reveal less than normal number of leukocytes (4000-10,000/cm) or white blood cells in the blood.
- Thrombocytopoenia: Total platelets count in the blood may be very low in dengue fever.
- Serum tests measure the antibody produced against dengue virus.
-

Who are at risk of developing the disease?
Dengue has become the most notable mosquito-borne disease of the 1990s. Each year tens of millions of people are affected by the disease. About 2.5 billion people live in areas that are at risk of an epidemic transmission.
The highest incidence of dengue is in Southeast Asia, India and the American tropics where Aedes aegypti can be found. Outbreaks are more common in tropical countries. Factors like overcrowding, open water storage and irrigation canals provide breeding grounds for mosquitoes. -
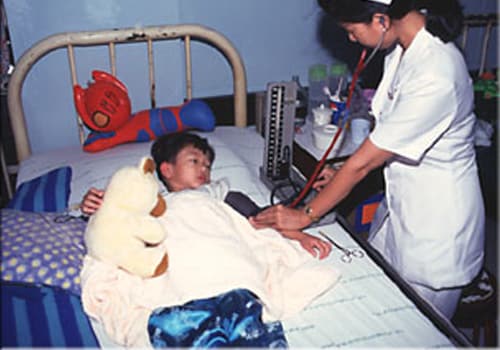
What is the treatment?
Treatment is only supportive in case of dengue fever, which means rest, plenty of fluids and acetaminophen to keep the temperature down. Hospitalisation may be required in severe cases to monitor the platelet count. If platelet count falls below a critical level (40,000/cm), it may be necessary to transfuse fresh blood or platelet rich plasma (PRP).
-

How can dengue be prevented?
Personal protection against mosquito bites should be done by using mosquito repellents, netting and wearing clothes that cover the body while going out. Care should be taken to see that there are no stagnating water bodies around the living areas and the surroundings are kept clean.

















