-
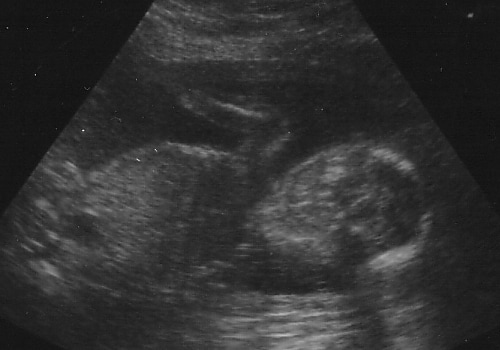
What is a miscarriage?
A miscarriage or spontaneous abortion usually occurs before the 20th week of pregnancy. It is a natural way for the body to expel a fetus that is not expected to successfully grow into a baby. Miscarriage has a fairly high rate since almost 10-20% pregnancies are miscarried by the 12 week.
Most miscarriages that occur in the first three months are due to abnormalities in the fetus. Miscarriages that occur in the second trimester are more often due to trauma to the mother. Miscarriage is different from abortion in that the latter is often used to refer to a pregnancy that is ended intentionally. -
What are the various types of miscarriages?
Miscarriages may be classified according to the stage at which they occur and the nature of the miscarriage.
- Missed miscarriage – when the miscarriage has occurred but there are no visible signs and the remains have not been expelled from the uterus.
- Incomplete miscarriage – when the contents of the uterus have not been expelled completely. A D&C may have to be done to clean the uterus.
- Complete miscarriage – when the remains have been expelled from the uterus completely.
- Inevitable miscarriage – when the fetus is malformed to continue as a viable pregnancy.
- Threatened miscarriage – when the signs of miscarriage are observed early in the pregnancy.
- Septic miscarriage – when infection occurs in the fetus before, during or after miscarriage.
- Missed miscarriage – when the miscarriage has occurred but there are no visible signs and the remains have not been expelled from the uterus.
-

How is it caused?
Though a miscarriage occurs when a pregnancy is not viable to be continued, there are some risk factors that predispose to miscarriage.
- Maternal age – the risk of a miscarriage increases with age. A woman is 20 times more likely to have a miscarriage at the age of 40 years than at 20.
- There is an increased risk if the woman has miscarried before or has had a stillborn child earlier.
- Women who suffer from diabetes, hypothyroidism or any other endocrinological disorder are at high risk.
- Diseases like systemic erythromatus lupus, uterine fibroids or endometriosis increase the risk.
- Conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), rubella, herpes, sexually transmitted infections (ST’s) etc. also increase the risk.
- An abrupt fall in the body hormones might lead to a miscarriage.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol, caffeine and cigarettes increases the risk.
- Abnormality in the shape of the uterus or weakness of the organ.
- Exposure to chemicals and other toxins.
- Physical trauma or injury, in some cases.
-

What are the symptoms?
The signs of a miscarriage are usually fairly obvious and can be easily discerned. Some of the common signs are:
- Abrupt vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
- Abdominal cramps alternating with continuous stomach ache
- Low back pain
- Expulsion of semi-solid matter from the vagina without pain.
-
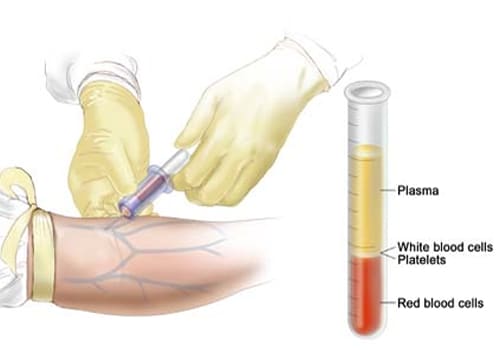
How is it diagnosed?
A blood and urine test confirms a pregnancy. The presence of a hormone HCG in the body confirms pregnancy and rising levels indicate that the fetus is growing healthily. Tests that may be done to check for an imminent miscarriage are:
- complete blood count (CBC)
- white blood cell count to identify an infection
- pregnancy ultrasound to check for fetal movement and heartbeat
- pelvic examination to check for traces of fetal tissue in the cervix or vagina.
-
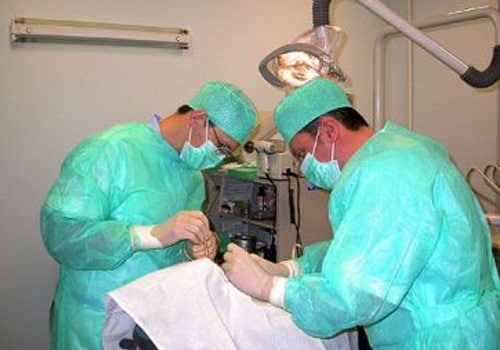
What is the treatment?
Except in case of a threatened miscarriage, the contents of the uterus have to be medically removed. A D&C is usually done by a gynaecologist to clean the uterus. The patient may be given antibiotics to prevent infection. Medications are given to help the uterus contract so that the bleeding reduces. For women in whom the miscarriage is caused by Rh incompatibility, Rh immunoglobulins are given to reduce the risk of miscarriage in subsequent pregnancies.
There may be some side effects of treatment like an allergic reaction to the anaesthesia, stomach upset, body rash, abdominal cramps and vaginal bleeding. In some women, there may be fever. The patient is usually sent home after regaining consciousness, but is advised complete bed rest for about 2 days. Exercise and sex is prohibited for sometime depending on her general health. -

How can it be prevented?
Miscarriages cannot usually be prevented but steps can be taken to reduce their chances. Some of the guidelines are:
- The diet should be rich in Vitamin B
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol
- Stop smoking completely during pregnancy
- Sexual promiscuity may lead to sexually transmitted infections, increasing the risk of miscarriage
- Special care should be taken if the pregnant lady is suffering from a disease.


















